Best ERP Software Guide: How to Choose the Best ERP Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software has become an integral tool for businesses aiming to streamline their operations, enhance productivity, and maintain a competitive edge in the market. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of ERP software, its importance in business operations, and key considerations for choosing the best ERP solution for your organization.
Understanding ERP
Definition of ERP
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a type of software used by organizations to manage and integrate the important parts of their businesses. An ERP software system can integrate planning, purchasing inventory, sales, marketing, finance, human resources, and more.
History and Evolution of ERP
The concept of ERP dates back to the 1960s when organizations started using software applications to manage business activities. Over the decades, ERP systems have evolved from standalone applications to complex, integrated systems that provide real-time data and insights across the entire organization.
The Origins of ERP: 1960s and 1970s
The origins of ERP systems can be traced back to the 1960s when large organizations began seeking ways to streamline their manufacturing processes. During this period, Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems emerged as the first precursor to modern ERP. MRP systems were designed to manage manufacturing processes, ensuring that materials and products were available for production and delivery. These systems focused on optimizing inventory levels and scheduling production processes, providing businesses with the tools needed to improve efficiency and reduce waste.
In the 1970s, MRP systems evolved into MRP II (Manufacturing Resource Planning) systems. MRP II expanded the scope of MRP by integrating additional manufacturing processes, such as production planning, scheduling, and capacity requirements planning. These systems provided more comprehensive solutions for managing manufacturing operations, incorporating financial and operational data to enhance decision-making and planning.
The Emergence of ERP: 1980s
The 1980s marked a significant turning point in the evolution of ERP systems. During this decade, the concept of integrating various business processes into a single system began to take shape. Companies started to recognize the benefits of having a unified system that could manage not only manufacturing processes but also other core business functions, such as finance, human resources, and supply chain management.
The term “Enterprise Resource Planning” was coined during this period to describe these comprehensive systems. ERP systems of the 1980s were primarily on-premise solutions, hosted on company servers and managed by internal IT departments. These early ERP systems were complex and expensive, making them accessible primarily to large corporations with substantial IT budgets.
ERP Expansion and Innovation: 1990s
The 1990s saw rapid advancements in ERP technology and widespread adoption across various industries. The development of more powerful and affordable computing hardware, coupled with the advent of client-server architecture, made ERP systems more accessible to a broader range of businesses.
During this decade, leading ERP vendors such as SAP, Oracle, and PeopleSoft emerged as key players in the market. These companies developed ERP systems that integrated a wide range of business functions, including finance, human resources, procurement, and sales. The introduction of graphical user interfaces (GUIs) and more user-friendly designs further facilitated the adoption of ERP systems.
The late 1990s also saw the emergence of industry-specific ERP solutions tailored to the unique needs of various sectors, such as manufacturing, retail, and healthcare. These specialized systems provided businesses with more targeted and effective tools for managing their operations.
The Rise of Cloud-Based ERP: 2000s
The early 2000s marked the beginning of a new era in ERP technology with the rise of cloud computing. Cloud-based ERP solutions, also known as Software as a Service (SaaS) ERP, offered businesses a more flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional on-premise systems. With cloud-based ERP, companies could access their ERP systems via the internet, eliminating the need for extensive hardware investments and reducing the burden on internal IT departments.
Cloud-based ERP systems provided numerous benefits, including lower upfront costs, easier scalability, automatic updates, and improved accessibility. These advantages made ERP systems more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), democratizing the use of ERP technology across businesses of all sizes.
Leading ERP vendors adapted to this new paradigm by developing cloud-based versions of their systems. For example, SAP introduced SAP Business ByDesign, while Oracle launched Oracle ERP Cloud. The shift to cloud-based ERP marked a significant milestone in the evolution of ERP technology, driving further innovation and adoption.
Modern ERP Systems: 2010s and Beyond
The 2010s witnessed continued advancements in ERP technology, driven by emerging trends such as mobile computing, big data, and advanced analytics. Modern ERP systems began to incorporate these technologies to provide businesses with more powerful and intelligent solutions for managing their operations.
Mobile ERP solutions enabled users to access their ERP systems from smartphones and tablets, enhancing flexibility and productivity. Big data and analytics tools allowed businesses to gain deeper insights into their operations, enabling data-driven decision-making and strategic planning.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into ERP systems further enhanced their capabilities. AI-powered ERP systems could automate routine tasks, predict trends, and provide intelligent recommendations, transforming how businesses operated and made decisions.
Today, ERP systems continue to evolve, with a focus on enhancing user experience (UX), integrating the Internet of Things (IoT), and providing more personalized and adaptive solutions. The future of ERP technology promises even greater advancements, with ongoing innovation driving the development of more intelligent, flexible, and powerful systems.
Key Milestones in the Evolution of ERP
- 1960s: Introduction of Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems.
- 1970s: Evolution to Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) systems.
- 1980s: Emergence of the term “Enterprise Resource Planning” (ERP) and the development of integrated systems.
- 1990s: Widespread adoption of ERP systems, introduction of industry-specific solutions, and rise of leading ERP vendors.
- 2000s: Advent of cloud-based ERP solutions, making ERP more accessible to businesses of all sizes.
- 2010s: Integration of mobile computing, big data, AI, and ML into ERP systems.
- 2020s and beyond: Continued advancements in UX, IoT integration, and the development of more intelligent and adaptive ERP solutions.
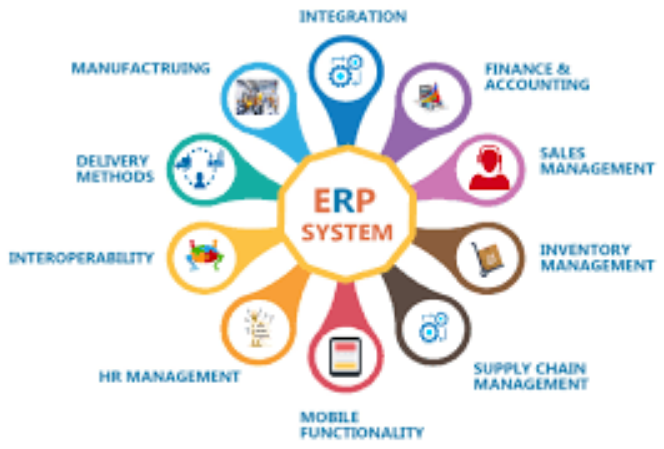
Core Components of ERP Systems
ERP systems typically include modules for financial management, human resources, supply chain management, customer relationship management, and business intelligence. These modules work together to provide a unified system that enhances information flow and decision-making processes.
Benefits of ERP
Improved Efficiency
ERP systems automate repetitive tasks and processes, reducing the time and effort required to manage business operations. This leads to increased efficiency and productivity.
Enhanced Reporting and Planning
With ERP, businesses can access real-time data and generate accurate reports that aid in strategic planning and decision-making.
Data Security and Integrity
ERP systems offer robust security features that protect sensitive business data from unauthorized access and breaches.
Scalability and Flexibility
ERP systems are scalable and can grow with your business. They also offer flexibility in terms of customization and integration with other software applications.
Types of ERP Systems
On-Premise ERP
On-premise ERP systems are installed on the company’s own servers and maintained by the company’s IT staff. These systems offer greater control but require significant investment in hardware and maintenance.
Cloud-Based ERP
Cloud-based ERP systems are hosted on the vendor’s servers and accessed via the internet. These systems offer lower upfront costs, easier updates, and greater accessibility.
Hybrid ERP
Hybrid ERP combines both on-premise and cloud-based solutions, offering the benefits of both approaches. This model allows businesses to keep certain critical applications on-premise while leveraging the flexibility and cost savings of the cloud for other functions.
Key Features to Look For
Financial Management
An ERP system should offer comprehensive financial management capabilities, including general ledger, accounts payable, accounts receivable, and financial reporting.
Human Resources Management
HR modules in ERP systems help manage employee records, payroll, benefits, performance evaluations, and recruitment processes.
Supply Chain Management
ERP systems should include features for managing procurement, inventory, production, and logistics to optimize the supply chain.
Customer Relationship Management
CRM modules help manage customer interactions, sales, marketing campaigns, and customer service to improve customer satisfaction and retention.
Inventory Management
Inventory management features help track stock levels, manage orders, and reduce excess inventory, ensuring that the right products are available at the right time.
Business Intelligence
BI tools in ERP systems provide data analytics and reporting capabilities that help businesses make informed decisions based on real-time data.
Industry-Specific ERP Solutions
Manufacturing ERP
Manufacturing ERP systems are designed to manage the complexities of production processes, including planning, scheduling, and quality control.
Retail ERP
Retail ERP systems help manage point-of-sale transactions, inventory, customer relationships, and supply chain operations specific to the retail industry.
Healthcare ERP
Healthcare ERP systems streamline patient management, billing, scheduling, and regulatory compliance, improving overall patient care.
Education ERP
Education ERP systems manage administrative processes, student information, enrollment, grades, and communication in educational institutions.
Construction ERP
Construction ERP systems assist with project management, budgeting, resource allocation, and compliance in the construction industry.
How to Choose the Best ERP
Assessing Business Needs
Identify the specific needs and challenges of your business to determine the essential features required in an ERP system.
Budget Considerations
Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including licensing, implementation, training, and maintenance costs, to ensure the ERP system fits within your budget.
Vendor Reputation and Support
Research potential ERP vendors’ reputation, customer reviews, and support services to choose a reliable and trustworthy partner.
Customization and Integration
Ensure the ERP system can be customized to meet your business needs and can integrate seamlessly with your existing software applications.
User-Friendliness and Training
Choose an ERP system that is user-friendly and provides comprehensive training and support to ensure smooth adoption by your team.
Future-Proofing and Upgrades
Consider the scalability and upgrade capabilities of the ERP system to ensure it can adapt to your business’s future growth and technological advancements.
ERP Implementation Process
Planning and Requirement Analysis
Begin with thorough planning and requirement analysis to define the scope and objectives of the ERP implementation project.
System Design and Configuration
Design and configure the ERP system to align with your business processes and requirements.
Data Migration and Testing
Migrate existing data to the new ERP system and conduct extensive testing to ensure accuracy and functionality.
User Training and Support
Provide comprehensive training to users and establish support mechanisms to facilitate a smooth transition to the new ERP system.
Go-Live and Evaluation
Go live with the ERP system and continuously monitor its performance, gathering feedback for further improvements.
Common Challenges in ERP Implementation
Data Migration Issues
Transferring data from legacy systems to the new ERP system can be complex and prone to errors, requiring careful planning and execution.
User Resistance
Employees may resist changes associated with ERP implementation, highlighting the need for effective change management and training.
Cost Overruns
ERP implementation projects can exceed budget due to unforeseen challenges and scope changes, necessitating diligent project management.
Inadequate Training
Insufficient training can lead to poor user adoption and underutilization of the ERP system, impacting its overall effectiveness.
Best Practices for Successful ERP Implementation
Clear Project Goals and Objectives
Define clear and achievable goals for the ERP implementation project to guide the process and measure success.
Strong Project Management
Ensure strong project management practices, including setting timelines, allocating resources, and monitoring progress.
Involving Key Stakeholders
Engage key stakeholders from various departments to gather input, address concerns, and foster buy-in for the ERP project.
Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Regularly monitor and evaluate the ERP system’s performance and make necessary adjustments to optimize its benefits.
ERP Trends and Future Prospects
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML technologies are enhancing ERP systems’ capabilities, enabling predictive analytics, automation, and smarter decision-making.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
IoT integration allows ERP systems to collect real-time data from connected devices, improving asset management and operational efficiency.
Mobile ERP Solutions
Mobile ERP solutions offer greater accessibility and flexibility, allowing users to access ERP functions from anywhere, anytime.
Enhanced User Experience (UX) Design
Modern ERP systems are focusing on intuitive and user-friendly interfaces to improve user experience and adoption rates.
Comparative Analysis
Leading ERP Vendors: SAP vs. Oracle vs. Microsoft Dynamics
A comparison of the top ERP vendors, including their features, strengths, and weaknesses, to help businesses make an informed decision.
Pros and Cons of Each Vendor
An in-depth analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics ERP systems.
Cost Comparison
A detailed comparison of the costs associated with each ERP vendor, including licensing, implementation, and ongoing maintenance.
ERP Case Studies
Successful ERP Implementation in a Manufacturing Company
A case study highlighting the successful implementation of an ERP system in a manufacturing company and its impact on operations.
ERP in Retail: A Success Story
An example of how a retail company leveraged ERP software to improve inventory management and customer service.
Healthcare ERP: Improving Patient Care
A case study demonstrating how a healthcare provider used ERP to streamline patient management and enhance care delivery.
ERP in Education: Streamlining Administration
An overview of how an educational institution implemented ERP to manage administrative processes and improve efficiency.
Construction ERP: Enhancing Project Management
A case study showcasing the benefits of ERP in managing construction projects, including resource allocation and budget control.
FAQs About ERP Software
What is ERP software?
ERP software is a suite of integrated applications that help organizations manage business processes and operations more efficiently.
How does ERP improve business efficiency?
ERP improves efficiency by automating tasks, integrating business functions, and providing real-time data for informed decision-making.
What are the costs associated with ERP implementation?
Costs include software licensing, hardware, implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance and support.
Can small businesses benefit from ERP?
Yes, ERP systems can be scaled to fit the needs of small businesses, offering significant efficiency and productivity gains.
How long does it take to implement an ERP system?
Implementation time varies based on the system’s complexity and the organization’s size, typically ranging from several months to a year.
What are the risks of ERP implementation?
Risks include data migration issues, cost overruns, user resistance, and inadequate training.
How to choose the right ERP vendor?
Consider factors such as business needs, budget, vendor reputation, customization options, and support services when selecting an ERP vendor.
Conclusion
Choosing the right ERP system is a critical decision that can significantly impact your business’s efficiency, productivity, and growth. By understanding your business needs, evaluating different ERP options, and following best practices for implementation, you can select an ERP solution that meets your organization’s unique requirements. For further learning, explore more resources and stay updated on the latest trends and innovations in ERP technology.