CRM vs. ERP In the world of business software, two acronyms often come up: CRM and ERP. But what do they mean, and why are they important? CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management, while ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. These systems are essential for managing different aspects of a business, but they serve distinct purposes. Understanding the difference between CRM and ERP can help businesses choose the right tools to enhance their operations.
What is CRM?
Definition and Purpose
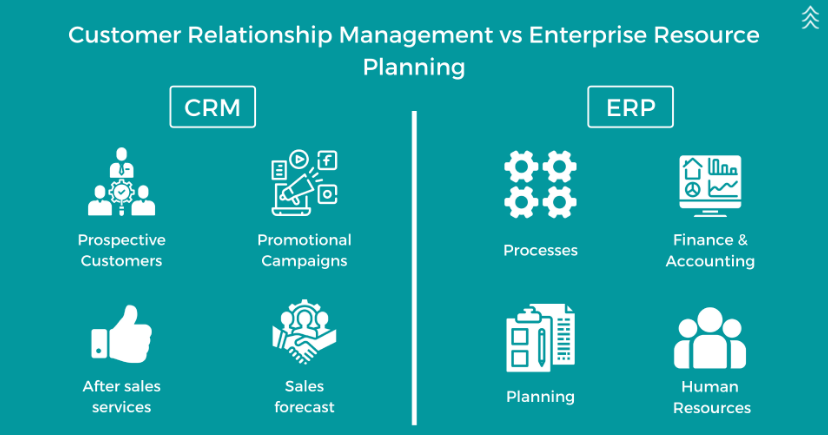
CRM, or Customer Relationship Management, is a technology used to manage interactions with customers and potential customers. The goal of CRM is to improve business relationships to grow your business. A CRM system helps companies stay connected to customers, streamline processes, and improve profitability.
Key Features of CRM Systems
CRM systems come with various features designed to manage customer relationships effectively:
- Contact Management: Organizes customer contact information.
- Sales Management: Tracks sales pipelines and opportunities.
- Customer Support: Manages customer service and support interactions.
- Marketing Automation: Automates marketing tasks and campaigns.
- Analytics: Provides insights into customer data and behavior.
Examples of Popular CRM Software
Some of the most widely used CRM software includes:
- Salesforce: A leading CRM platform known for its extensive features and customization options.
- HubSpot CRM: Offers a free CRM with essential features, ideal for small businesses.
- Zoho CRM: Provides a comprehensive suite of CRM tools at a competitive price.
What is ERP?
Definition and Purpose
ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning, is a type of software used by organizations to manage day-to-day business activities such as accounting, procurement, project management, and manufacturing. ERP systems integrate these various functions into one complete system to streamline processes and information across the organization.
Key Features of ERP Systems
ERP systems typically include the following features:
- Financial Management: Manages accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Supply Chain Management: Oversees procurement, inventory, and distribution.
- Human Resources Management: Handles employee records, payroll, and benefits.
- Manufacturing Management: Tracks production planning and execution.
- Project Management: Manages project planning, execution, and tracking.
Examples of Popular ERP Software
Some of the most widely used ERP software includes:
- SAP ERP: Known for its robust features and scalability for large enterprises.
- Oracle ERP Cloud: Offers a comprehensive suite of ERP applications in the cloud.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365: Combines ERP and CRM capabilities in one platform.
Core Differences Between CRM and ERP
Focus Areas: Customer vs. Enterprise
The primary difference between CRM and ERP lies in their focus areas. CRM is focused on managing customer interactions and improving customer relationships, while ERP is focused on managing the entire business operations to enhance efficiency and productivity.
Functional Scope
CRM systems are primarily used by sales, marketing, and customer service teams to manage customer data and interactions. In contrast, ERP systems are used across various departments, including finance, HR, supply chain, and manufacturing, to manage and integrate all business processes.
Data Management and Usage
CRM systems focus on collecting and analyzing customer data to enhance customer relationships and drive sales. ERP systems, on the other hand, focus on integrating and managing data from all business functions to improve overall business operations and decision-making.
Benefits of Using CRM
Enhancing Customer Relationships
CRM systems help businesses build and maintain strong relationships with customers by providing tools to manage interactions, track customer preferences, and personalize communications.
Improving Sales and Marketing Efforts
By providing insights into customer behavior and sales trends, CRM systems enable businesses to tailor their sales and marketing strategies to target the right customers with the right messages at the right time.
Increasing Customer Retention
CRM systems help businesses identify and address customer issues promptly, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty, which in turn leads to higher customer retention rates.
Benefits of Using ERP
Streamlining Business Processes
ERP systems streamline and automate business processes, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing errors, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
Integrating Various Business Functions
By integrating various business functions into one system, ERP systems provide a holistic view of the organization, enabling better coordination and decision-making.
Enhancing Efficiency and Productivity
With ERP systems, businesses can optimize resource utilization, improve process efficiency, and reduce operational costs, ultimately enhancing overall productivity.
How CRM and ERP Complement Each Other
Integrated Approach to Business Management
When used together, CRM and ERP systems provide a comprehensive solution for managing both customer-facing and back-end operations, ensuring seamless coordination across the organization.
Bridging the Gap Between Customer-Facing and Back-End Operations
Integrating CRM and ERP systems enables businesses to align their customer-facing activities with back-end processes, ensuring that customer needs are met efficiently and effectively.
Case Studies of Successful Integration
Many businesses have successfully integrated CRM and ERP systems to enhance their operations. For example, a retail company might use CRM to manage customer interactions and ERP to handle inventory and order fulfillment, ensuring that customer orders are processed and delivered promptly.
Choosing Between CRM and ERP
Assessing Business Needs and Goals
The decision to choose between CRM and ERP depends on the specific needs and goals of the business. If the primary focus is on improving customer relationships and sales, a CRM system might be the best choice. If the goal is to streamline and integrate all business processes, an ERP system might be more suitable.
Factors to Consider: Company Size, Industry, Budget
When choosing between CRM and ERP, businesses should consider factors such as company size, industry, and budget. Small businesses with limited resources might opt for a CRM system to focus on customer relationships, while larger enterprises might benefit from the comprehensive features of an ERP system.
When to Implement CRM, ERP, or Both
In some cases, businesses might find it beneficial to implement both CRM and ERP systems. For example, a growing company might start with a CRM system to manage customer interactions and later integrate an ERP system to streamline back-end operations as the business expands.
Challenges in Implementing CRM
Common Obstacles
Implementing a CRM system can present challenges such as resistance to change, data migration issues, and lack of user adoption. Addressing these obstacles requires careful planning and communication.
Tips for Successful Implementation
To ensure successful CRM implementation, businesses should involve key stakeholders in the process, provide adequate training to users, and continuously monitor and optimize the system to meet evolving needs.
Challenges in Implementing ERP
Common Obstacles
ERP implementation can be complex and time-consuming, with challenges such as high costs, integration issues, and disruption to business operations. It is essential to approach ERP implementation with a clear strategy and realistic expectations.
Tips for Successful Implementation
Successful ERP implementation requires thorough planning, involvement of all relevant departments, and continuous support and training. It is also crucial to choose an ERP system that aligns with the specific needs of the business.
Future Trends in CRM
Emerging Technologies
The future of CRM is likely to be shaped by emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and predictive analytics. These technologies can provide deeper insights into customer behavior and enhance the personalization of customer interactions.
Impact on Customer Experience
With advancements in CRM technology, businesses can offer more personalized and seamless customer experiences, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Future Trends in ERP
Emerging Technologies
The future of ERP will be influenced by technologies such as cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain. These technologies can enhance the functionality and scalability of ERP systems, making them more adaptable to changing business needs.
Impact on Business Processes
As ERP systems evolve, they will continue to streamline business processes and improve efficiency, enabling businesses to respond more quickly to market changes and customer demands.
Case Studies
Successful CRM Implementations
Several companies have successfully implemented CRM systems to enhance customer relationships and drive sales. For example, a telecommunications company might use CRM to track customer interactions and preferences, enabling personalized marketing campaigns that increase customer engagement and retention.
Successful ERP Implementations
Successful ERP implementations can significantly improve business operations. For instance, a manufacturing company might use ERP to integrate production planning, inventory management, and financial reporting, resulting in more efficient and cost-effective operations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both CRM and ERP systems play crucial roles in modern business management. While CRM focuses on improving customer relationships and driving sales, ERP aims to streamline and integrate all business processes. By understanding the core differences and benefits of each system, businesses can make informed decisions about which tools to implement based on their specific needs and goals. Whether choosing CRM, ERP, or a combination of both, the key is to align the chosen system with the overall business strategy to achieve optimal results.